Going green doesn’t have to cost more. Experts at the NAHB Research Center have identified design and construction tactics that builders have used to minimize the cost premium for green.
Constructing a green home does come with some added costs, but a lot of builders find that green practices can actually reduce their construction costs and enhance the quality of the homes they build. Many green practices also result in operational and maintenance savings for homeowners.
Using a combination of input from builders participating in the National Green Building Certification Program and results from recent research we did for HUD on the costs and benefits of green affordable housing, the NAHB Research Center has identified seven beneficial practices to consider when building green for the affordable market.
1. Work closely with your suppliers
If you’re new to green building in general or to building green homes with a lower price point, you may want to start your journey by talking with your product suppliers.
Richmond, Va.-based First Richmond Associates has been building quality workforce housing for nearly two decades. Recently, the builder decided that going green with its homes would provide even greater value to customers and set its product apart from the competition. Susan Hadder, president of First Richmond, admits the company didn’t know much about green building, so she let her suppliers know about the new direction they were taking and asked for their help.
“A lot of them were as new to green as we were,” says Hadder, “but they were excited to help us find the best product options available from various manufacturers. It was kind of fun for everyone to discover something new.”
Hadder says she got very quick responses from all her product reps, along with some incentives, which helped her identify what the company needed to get its new green homes certified to the National Green Building Standard (ICC 700). She was pleasantly surprised to find that many of the green product options that would garner points for the home in the certification process were actually an even swap for her in terms of price.
Specifically with flooring options, she found that recycled-content carpet and padding, engineered hardwood flooring, and recycled tile for the bathrooms were all competitively priced with the products she traditionally used — some a few pennies more per unit, some a few pennies less. First Richmond now has two of their Earth-Friendly workforce homes (sales prices range from the $170,000’s to low $200,000’s) Green Certified to ICC 700 by the NAHB Research Center, and the company has plans for more.
2. Look for two-for-one green product benefits
To maximize green benefits while keeping construction costs low, use products or practices with multiple green features. For example, when specifying cabinets or cabinet materials, look for those that have low- or no-formaldehyde content and are made of recycled material. That way, you may be able to gain green certification points for both indoor environmental quality and resource efficiency. While most green rating systems won’t allow for “double dipping” on points (i.e., claiming points in more than one area for the same green attribute in the same product or practice), most will allow for multiple green attributes in the same product to be counted across multiple point categories.
3. Don’t forget about water efficiency
In our work with HUD, we found that water efficiency improvements for both new and renovated affordable projects are commonly overlooked even though they offer a quantifiable benefit to homeowners for little to no additional construction cost. Be sure not to discount the cost benefits for affordable clients of low-flow faucets, toilets, and showerheads, as well as rated water-saving appliances.
As for finding the products at an affordable price, there is a much wider array of low-flow toilets, faucets, and showerheads on the market today than even five years ago, and the most basic models are cost neutral with comparable non-low-flow fixtures. Most major plumbing product manufacturers now offer these products, eliminating the need for costly special orders, in most cases. With bathroom sink faucets, even if your manufacturer of choice doesn’t make a low-flow version, you can buy replacement aerators that satisfy the requirements of most national green rating systems for around $2 a piece.

New construction on the Goose Pasture Tarn in Blue River, Colorado outside of Breckenridge.
4. Consider alternative framing techniques
Some changes in your framing materials or techniques might provide both cost/time savings and a means to an end in securing points toward green certification. For instance, consider using panels or trusses in lieu of site-built systems. These techniques are labor and resource efficient, resulting in less on-site waste and possibly lower labor and materials cost overall. Fabricated systems often create greater thermal efficiency over stick frames. Many green rating systems, including the National Green Building Standard, also award points for use of panels and trusses.
If you want to continue framing totally on site, there are several optimum value engineering (OVE) techniques that can save on material or labor costs, and can generate green points at the same time. Look into options like:
- Ladder blocking — uses less wood; provides more room for insulation; gets green points
- Two-stud corners — at least one less stud at each corner; allows for more fully insulated corner; gets green points
- Switch from 2x4s at 16 inches on center to 2x6s at 24 inches on center — may result in small increase in incremental cost initially, but gets a lot of green bang for your buck.
5. Explore low-cost strategies with design
Green, at any price point, is not accomplished through product selection alone. Many of the other “ingredients” for a green home involve strategies that can cost very little or nothing at all. For example, depending on the orientation and size of your lot, flipping a house plan is a very low-cost, low-effort activity that can result in green benefits like positioning the majority of windows on the south side of a home for passive solar and natural lighting gains.
6. Pay attention to placement and sizing of hvac and plumbing systems
Optimize your duct runs and centrally locate your mechanical room for material cost savings and increased energy efficiency. Even for smaller homes, be sure not to have more ducts or longer duct runs than you need in any part of the house. Using a central return also reduces material costs and is a simple system that can provide adequate circulation and cost savings to both you and your buyers.
Placing all your HVAC equipment, including ducts, in conditioned space within the home is also beneficial. In addition to creating significant energy savings for homeowners, this practice may also allow you to spec smaller, less-expensive HVAC equipment and limit or eliminate the need for additional insulation for the duct system. Many homes today, even those that may be otherwise energy and resource efficient, have oversized HVAC equipment. As the building envelope of your homes becomes tighter and more energy efficient, the HVAC burden is significantly reduced. A smaller system obviously costs less and could offset other green upgrades you’re making in your homes.
For your plumbing system, make sure you have chosen the most efficient design for your purposes. For multi-story homes, consider a stacked system, which will probably require shorter plumbing runs, less piping, and possibly less labor time from your plumbing contractor. Also consider centrally locating your water heater, as a central location makes the average of every run shorter, thereby reducing material costs.
7. Rely on green design professionals
Green homes often require a higher degree of precision in their design and construction to ensure that the finished product works the way it was designed to work, as a whole house relying on interdependent systems for its optimum efficiency and homeowner comfort. Having experts well versed in green products, practices, and protocols can save you thousands of dollars in trial-and-error and callbacks in the long run.
That being said, there are different ways to go about creating your design team. One way is to seek out experts in areas such as mechanical systems, plumbing design, and landscape architecture, with specific expertise in green building practices. Another tactic is to rally those with whom you already work to the pursuit of greener, more efficient homes. Similar to the enthusiasm and excitement Susan Hadder generated with her suppliers when First Richmond began seeking green solutions, you may generate the same kind of interest with your existing construction partners to learn all they can and contribute. Either way, it’s important to get everyone in your construction chain on the same page with what you’re trying to accomplish. Contractors and suppliers that are not informed can create inadvertent barriers to your ultimate success.
More information and technical detail about these techniques can be found on the Research Center’s technical website,www.ToolBase.org.
Created in 1964, the NAHB Research Center (www.nahbrc.com) is a full-service product commercialization company that strives to make housing more durable, affordable, and efficient. The Research Center provides public and private clients with an unrivaled depth of understanding of the housing industry and access to its business leaders.
Source : Professional Builder
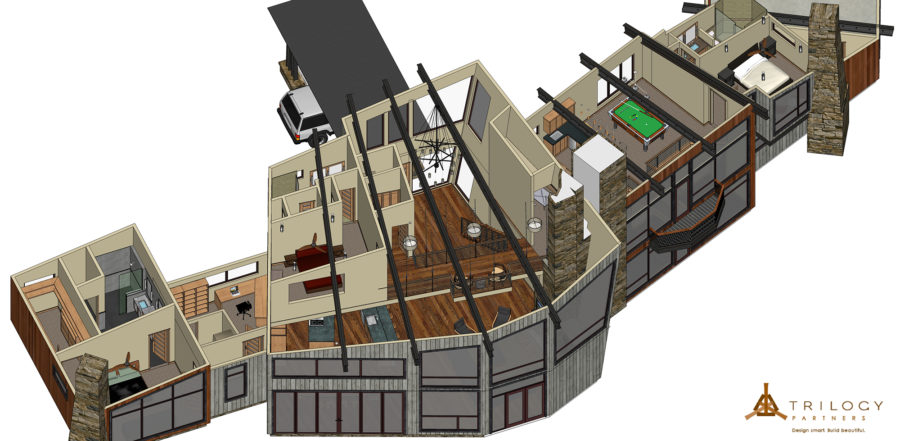
Extreme remodel on the Goose Pasture Tarn in Blue River, Colorado




















